Science
Researchers Uncover Vulnerabilities of Shield Tunnels Under Surcharge
In an important advancement in urban underground engineering, a team from Tongji University has conducted a comprehensive analysis of shield tunnels under surcharge loading. Their research highlights the significant risks posed by accidental surcharge, a man-made hazard that can severely compromise the structural integrity of metro systems. This study is particularly relevant for cities relying on underground transit, where safety is paramount.
The research, titled “Vulnerability Analysis of Shield Tunnels Under Surcharge Loading,” addresses a notable gap in existing studies, which have primarily focused on seismic threats. The team identified that current analyses often rely on singular damage indicators, leading to potentially misleading outcomes. Additionally, many studies fail to incorporate the uncertainties associated with soil parameters and tunnel burial depths, hindering their practical application.
Innovative Assessment Framework Developed
To tackle these challenges, the research team established a new vulnerability assessment framework. This framework evaluates the damage state of shield tunnels subjected to sudden extreme surcharges, taking into account both soil variability and the depth at which tunnels are buried. Using ABAQUS, a two-dimensional numerical model was created to simulate shield tunnels in soft soil under surcharge conditions, with results verified through field monitoring data.
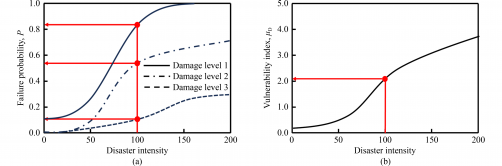
The researchers defined several damage indices, focusing on joint opening at key locations—Joint 1 at the tunnel crown, Joint 2 at the springline, and Joint 3 at the invert—alongside horizontal convergence. Each of these indices was classified into distinct damage states, ranging from none to collapse. The team then employed Monte Carlo calculations to generate fragility curves, which estimate the probability of exceeding specific damage states, and vulnerability curves, which reflect expected damage levels. The accuracy of these curves was ensured by fitting logistic functions for fragility curves and hyperbolic tangent functions for vulnerability curves, achieving a fitting accuracy with R² values near 1.
Key Findings and Real-World Application
The study’s extensive analysis of tunnels at various depths—shallow (8 m), moderately deep (16 m), and deep (30 m)—yielded critical insights. Notably, Joint 2 exhibited the highest likelihood of failure under the same surcharge conditions. The data revealed that moderately deep tunnels show increased vulnerability when surcharge levels exceed 50 kPa, while deep tunnels, despite facing greater soil and water pressure, are less affected by surcharge increases. Furthermore, the vulnerability index based on horizontal convergence was found to be more indicative of potential damage than that of Joint 1 as surcharge levels rise.
The practical implications of this research were demonstrated through its application to a real-world scenario involving the Shanghai Metro Line 2. The framework enabled rapid identification of high-risk sections, specifically ring numbers 350–390 and 550–590. Based on the assessed vulnerability levels, the team recommended targeted measures, such as grouting and the installation of bonded AFRP or steel plates, to enhance structural safety.
The findings of this vital research, authored by Zhongkai Huang, Hongwei Huang, Nianchen Zeng, and Xianda Shen, underscore the importance of comprehensive vulnerability assessments in urban infrastructure. The full text of the paper is available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11709-025-1193-4.
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoUrgent Update: Tom Aspinall’s Vision Deteriorates After UFC 321
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoMIT Scientists Uncover Surprising Genomic Loops During Cell Division
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Enhance Disaster Monitoring
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoAI Disruption: AWS Faces Threat as Startups Shift Cloud Focus
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHoneywell Forecasts Record Business Jet Deliveries Over Next Decade
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoDiscover the Full Map of Pokémon Legends: Z-A’s Lumiose City
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoGOP Faces Backlash as Protests Surge Against Trump Policies
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoParenthood Set to Depart Hulu: What Fans Need to Know
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Signals Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYoshinobu Yamamoto Shines in Game 2, Leading Dodgers to Victory
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMaine Insurers Cut Medicare Advantage Plans Amid Cost Pressures







