Science
Ultrasound-Activated Artificial Muscles Revolutionize Robotics
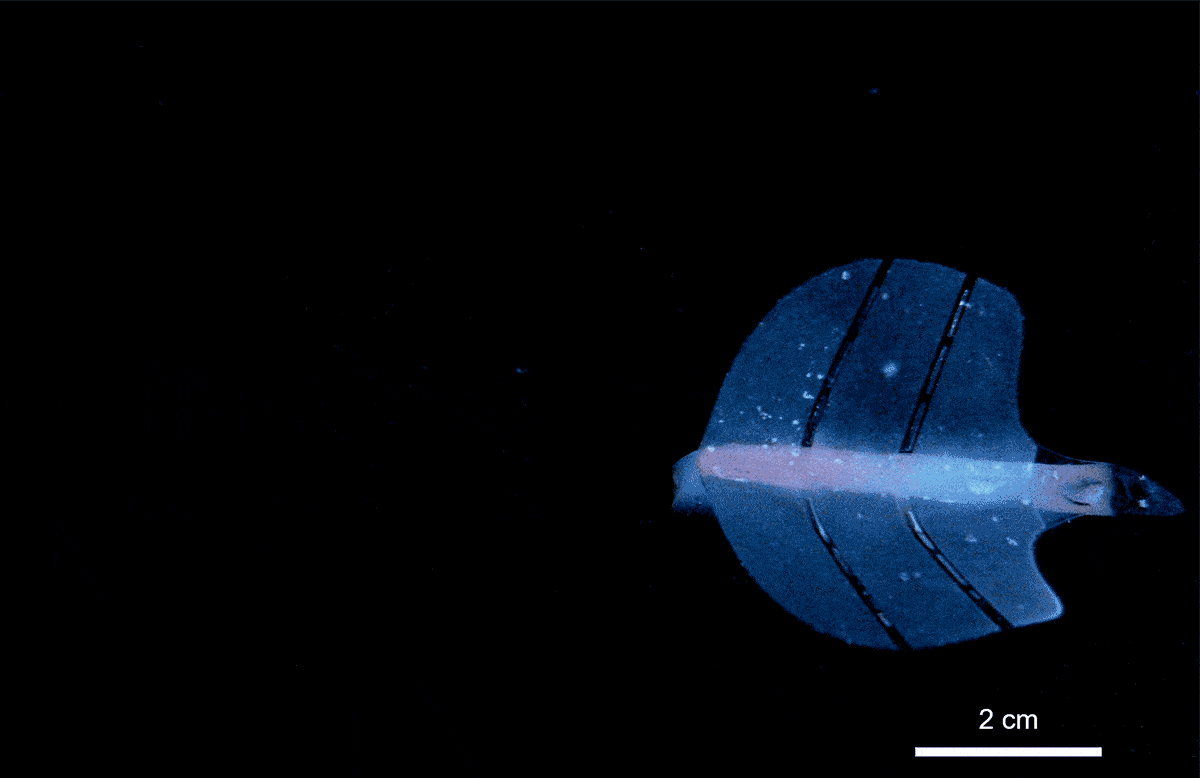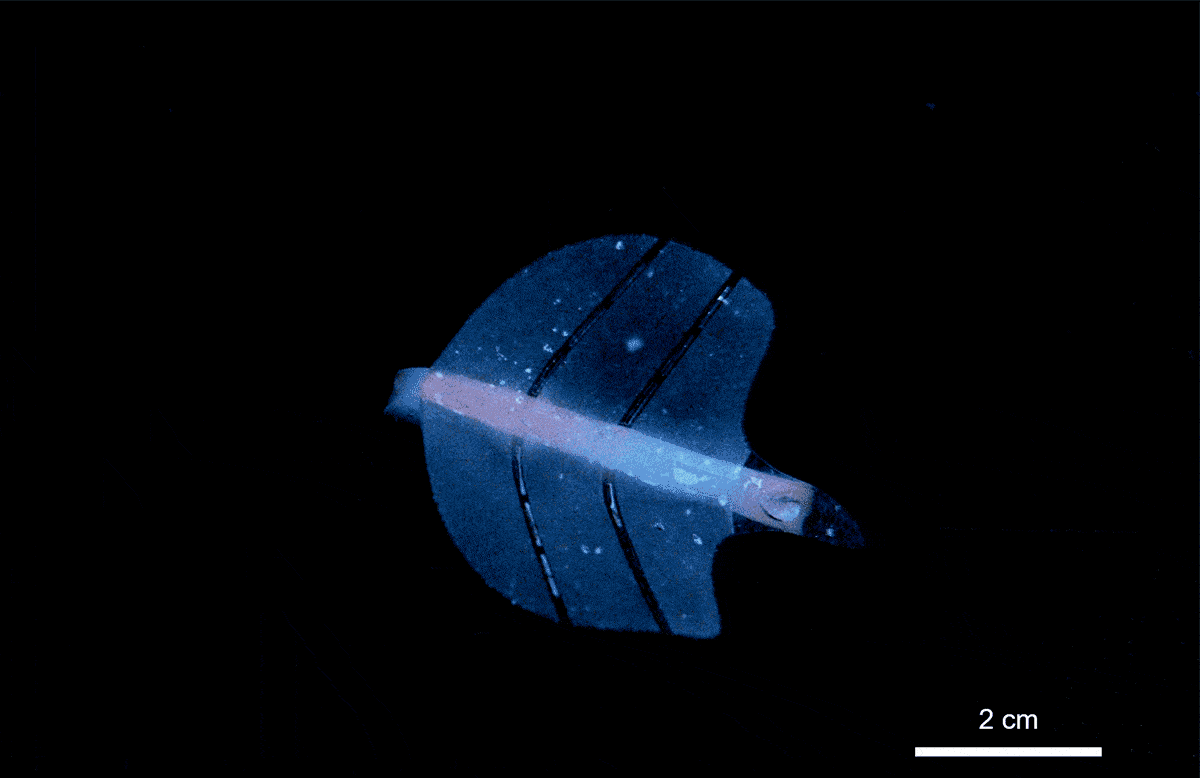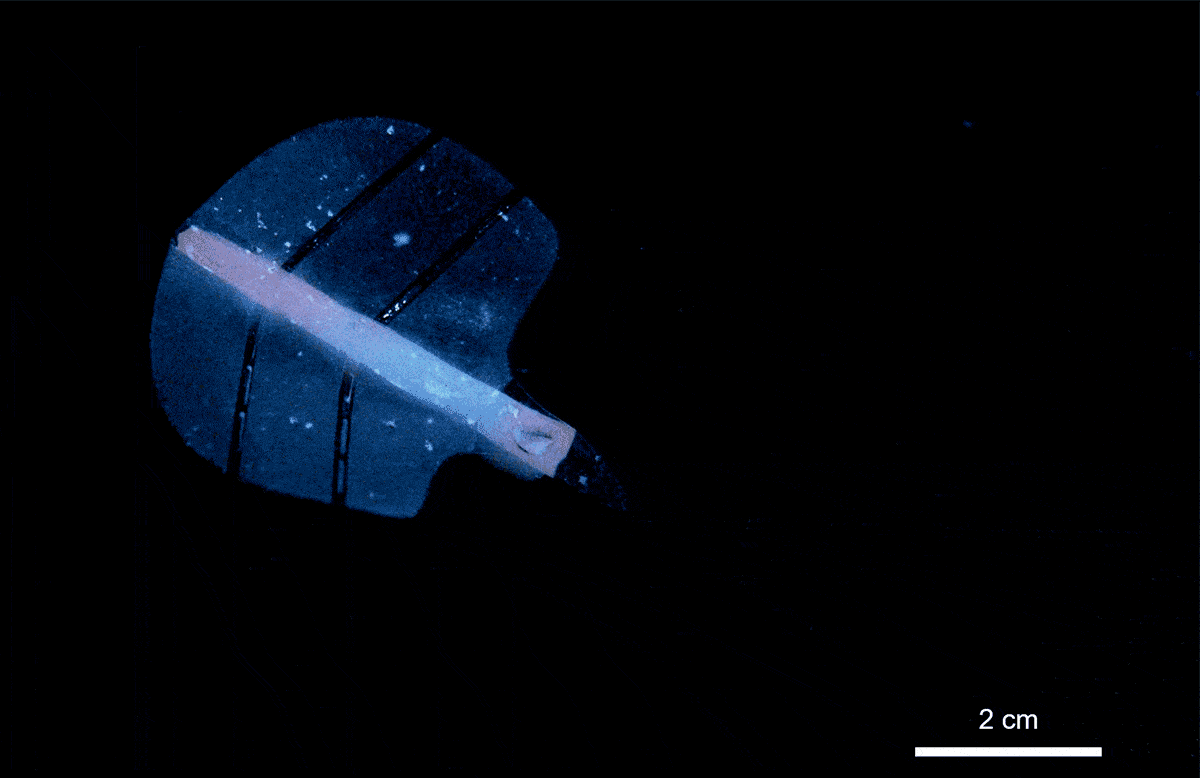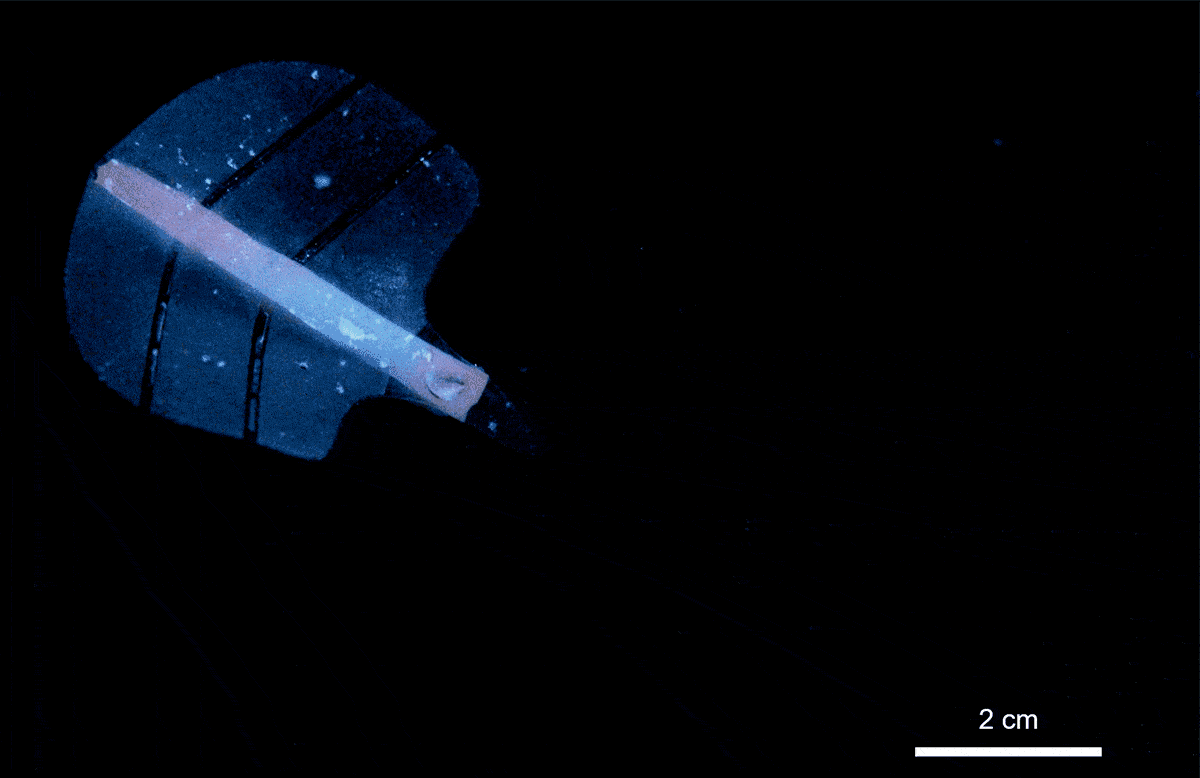
Researchers at ETH Zürich have developed a groundbreaking artificial muscle technology that utilizes ultrasound to create movements similar to those of natural muscles. This innovative approach, detailed in the journal Nature on March 15, 2024, involves a soft gel filled with microscopic bubbles that respond dynamically to sound waves. The implications of this discovery extend to various fields, including robotics and medicine.
The concept behind these “bubble muscles” is simple yet effective. When exposed to specific ultrasound frequencies, the embedded bubbles in the gel contract, grip, and lift with remarkable strength. This wireless method of actuation offers advantages over traditional artificial muscles, which often rely on motors or hydraulics that can be cumbersome and less efficient. According to Daniel Ahmed, a nanoroboticist at ETH Zürich, this new technology allows for programmable muscle movements through the manipulation of ultrasound frequencies.
Potential Applications in Robotics and Medicine
The potential applications of ultrasound-activated artificial muscles are vast. In experiments, researchers created a claw-like gripper capable of safely closing around live zebrafish larvae without causing harm. Additionally, they designed a stingray-inspired soft robot that moved fluidly through water, demonstrating the technology’s ability to navigate tight spaces with agility.
One significant highlight of Ahmed’s research involves the use of biocompatible materials. During trials using pig tissue, a patch of the bubble-patterned gel adhered to a pig heart for over an hour while responding to ultrasound. This capability suggests future uses in medical devices that require precise movements inside the human body.
“From a medical perspective, it’s really cool,” said Ryan Truby, a materials scientist at Northwestern University who did not participate in the study. He emphasized the clever integration of simple approaches to achieve complex functions.
Another innovative application involves encapsulating the artificial muscle material in a biodegradable capsule. When placed inside a pig bladder, the capsule dissolved, allowing ultrasound to activate the device, which then unfurled and adhered to the inner tissue wall. This could pave the way for targeted drug delivery systems in the future.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising results, challenges remain in adapting this technology for living organisms. All current tests have been conducted on deceased tissues, and researchers acknowledge that the performance of these bubble muscles in vivo is unproven. The complexity of human anatomy, including bones and irregular tissues, may interfere with ultrasound signals, complicating control.
W. Hong Yeo, a bioengineer at Georgia Tech who was not involved in the research, pointed out that the system’s effectiveness cannot be fully validated without in vivo evidence. Additionally, prolonged activation can cause the bubbles to expand, potentially destabilizing their function after about half an hour of use.
Nevertheless, the rapid responsiveness and small scale of these bubble muscles make them an attractive option for biomedical implants. As research progresses, further exploration into the integration of this technology into medical and robotic applications could lead to significant advancements in both fields.
The development of ultrasound-activated artificial muscles marks a significant step forward in the quest for more efficient and effective robotic systems, as well as innovative medical solutions that could enhance patient care and treatment outcomes.
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoUrgent Update: Tom Aspinall’s Vision Deteriorates After UFC 321
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoMIT Scientists Uncover Surprising Genomic Loops During Cell Division
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Enhance Disaster Monitoring
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoAI Disruption: AWS Faces Threat as Startups Shift Cloud Focus
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHoneywell Forecasts Record Business Jet Deliveries Over Next Decade
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoDiscover the Full Map of Pokémon Legends: Z-A’s Lumiose City
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoGOP Faces Backlash as Protests Surge Against Trump Policies
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoParenthood Set to Depart Hulu: What Fans Need to Know
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Signals Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYoshinobu Yamamoto Shines in Game 2, Leading Dodgers to Victory
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMaine Insurers Cut Medicare Advantage Plans Amid Cost Pressures







