Health
Researchers Discover p53 Mutations Could Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy
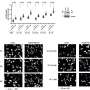
A recent study from researchers at Baylor College of Medicine has unveiled critical insights about specific mutations of the p53 gene and their potential to enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy in cancer treatment. The gene, often referred to as the guardian of the genome, is vital for maintaining genomic stability and preventing the development of tumors. However, when mutated, p53 can contribute to cancer progression by enabling aggressive growth of cancer cells.
Published in Communications Biology, the study focuses on two common p53 mutations, R273H and R175H, and their distinct effects on cancer cell behavior. According to Dr. Weei-Chin Lin, the corresponding author and a professor at Baylor, their investigation revealed that the R273H mutation not only promotes excessive DNA replication but also triggers a robust immune response against the cancer cells.
Understanding the Impact of p53 Mutations
The researchers conducted experiments to understand how these mutations affect DNA replication, which is a crucial step in cancer cell proliferation. The R273H mutation was found to lead to heightened DNA replication, thereby accelerating tumor growth. Surprisingly, this excessive replication also initiated a strong immune response via the activation of the cGAS-STING pathway, a key component of the body’s innate immune system.
In contrast, the R175H mutation, while also promoting cancer growth, did not elicit any immune response. This finding underscores the necessity of identifying the specific p53 mutation present in each patient’s tumor, as it may significantly influence both the tumor’s behavior and the therapeutic strategies employed.
Potential for Personalized Cancer Treatments
The team further explored the implications of their findings in mouse models of breast cancer. They investigated whether tumors harboring the R273H mutation would respond more favorably to immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of therapies that enhance the immune system’s ability to combat cancer. The results were promising; tumors with the R273H mutation treated with these inhibitors showed an increase in CD8+ T cells, which are crucial for attacking cancer cells, indicating an active immune response against the tumors.
These discoveries could significantly impact cancer therapy strategies. Although immune checkpoint inhibitors have transformed treatment for various cancers, their effectiveness is not universal. Dr. Lin highlighted the potential for utilizing p53 mutation profiling to predict which patients might benefit most from immunotherapy. “Our study suggests that identifying tumors with mutant p53 variants like R273H may allow doctors to tailor treatments more effectively,” he stated.
Moreover, the research hints at the possibility of enhancing immunotherapy by combining it with drugs that target DNA replication, which could further strengthen the immune response in susceptible patients. These findings pave the way for new avenues in personalized cancer treatment, offering hope for more effective therapies for those affected by this disease.
The collaborative effort by Kang Liu, Lidija A. Wilhelms Garan, and Fang-Tsyr Lin, along with Dr. Lin, marks a significant step in understanding the complex interplay between genetic mutations and cancer therapy. As research continues, the implications for clinical practice could reshape how oncologists approach treatment for patients with specific p53 mutations, ultimately aiming for improved outcomes in cancer care.
For more information, refer to the publication by Kang Liu et al, titled “Mutant p53 variants differentially impact replication initiation and activate cGAS-STING to affect immune checkpoint inhibition,” in Communications Biology (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-09050-3.
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoUrgent Update: Tom Aspinall’s Vision Deteriorates After UFC 321
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoMIT Scientists Uncover Surprising Genomic Loops During Cell Division
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Enhance Disaster Monitoring
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoAI Disruption: AWS Faces Threat as Startups Shift Cloud Focus
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHoneywell Forecasts Record Business Jet Deliveries Over Next Decade
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoDiscover the Full Map of Pokémon Legends: Z-A’s Lumiose City
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoGOP Faces Backlash as Protests Surge Against Trump Policies
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoParenthood Set to Depart Hulu: What Fans Need to Know
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Signals Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYoshinobu Yamamoto Shines in Game 2, Leading Dodgers to Victory
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMaine Insurers Cut Medicare Advantage Plans Amid Cost Pressures







