Science
Scientists Uncover Ancient Secrets and Cosmic Wonders This Week
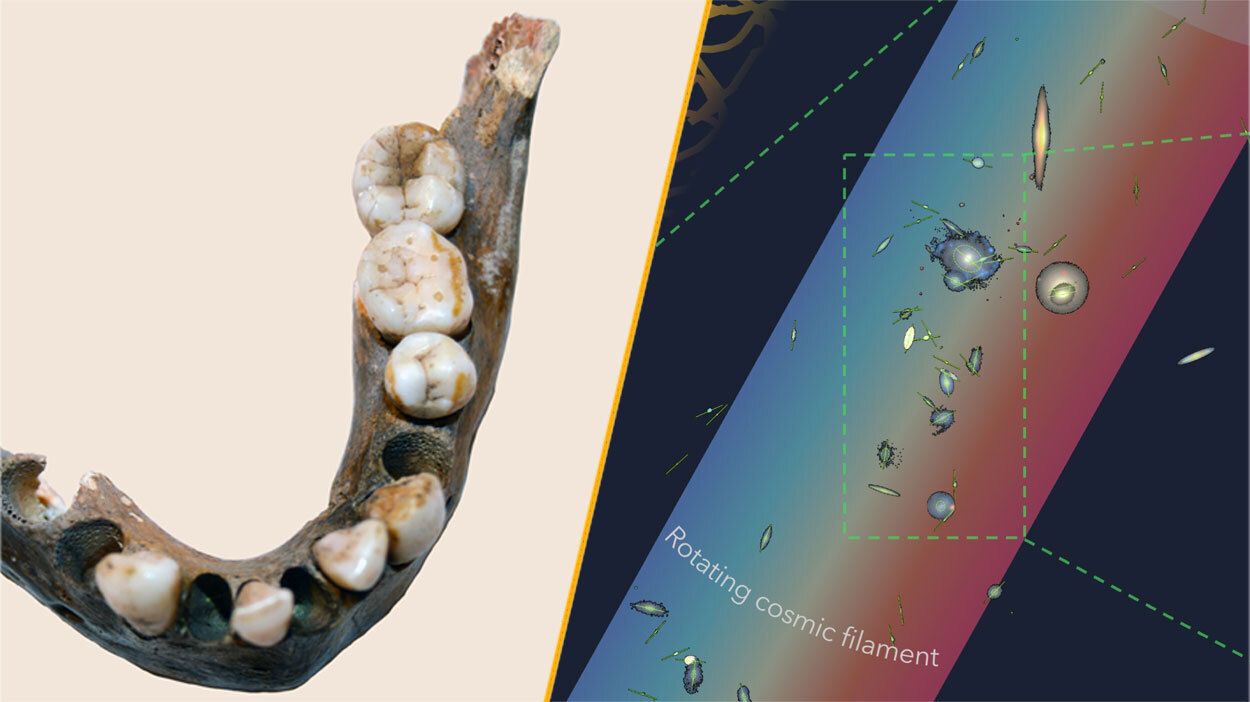
This week, significant scientific discoveries have emerged from across the globe, revealing insights into human history, cosmic phenomena, and modern technology. Key findings include the identification of the largest spinning object in the universe, a human population that remained genetically isolated for 100,000 years, and groundbreaking advancements in water extraction technology.
Cosmic Discovery: The Largest Spinning Structure
Astronomers have identified what may be the largest spinning structure in the universe, located approximately 140 million light-years from Earth. This colossal rotating filament, part of a daisy-chain of 14 galaxies, spans a width greater than that of the Milky Way. It is rotating at an impressive speed of around 68 miles per second (110 kilometers per second). The discovery was made possible through observations that traced the filament’s connection to these galaxies, showcasing the immense scale of cosmic structures.
Ancient Human Isolation and Modern Implications
Closer to Earth, a recent genetic study focused on a human population in southern Africa that was isolated for 100,000 years. Researchers examined skeletons dating back up to 10,000 years, found south of the Limpopo River, which flows from South Africa into Mozambique. The findings reveal that these ancient individuals exhibited a genetic makeup significantly different from that of contemporary humans. According to the study, these individuals represent “an extreme end of human genetic variation,” highlighting the diverse evolutionary paths taken by human populations.
In a parallel exploration of ancient practices, archaeologists in China uncovered a pit filled with skulls near a city that dates back 4,000 years. This discovery has raised questions due to the predominance of male skulls, deviating from sacrificial patterns typically observed in surrounding regions. Additionally, a 2,700-year-old tomb in Greece, featuring a woman adorned with an upside-down crown, has further intrigued researchers, prompting discussions about burial customs and gender roles in ancient societies.
Modern Challenges: Ecosystem Engineering and Water Extraction
In contemporary environmental news, a major tree-planting initiative in China, part of the Great Green Wall project aimed at combating desertification, has produced unintended consequences. While the project has successfully halted the spread of desert land, it has altered rainfall and evaporation patterns, leading to lower water levels in some of the country’s most populous areas, as highlighted in a recent analysis.
Technological advancements also emerged this week, with researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) announcing a novel method to extract drinking water from the air. This innovative technique utilizes ultrasound waves to extract water vapor efficiently, achieving results 45 times faster than traditional evaporation methods. While the device requires a power source, the team believes it could be paired with solar cells to overcome this challenge.
In a striking revelation, researchers have suggested that the record-high temperature recorded in Death Valley in 1913 may have resulted from human error, raising questions about historical climate data accuracy. Furthermore, scientists warn that the collapse of a key Atlantic current could usher in centuries of drought across Europe, highlighting the ongoing challenges posed by climate change.
Exploring the Cosmos and Unraveling Mysteries
The fascination with interstellar phenomena continues, as comet 3I/ATLAS has been observed exhibiting “ice volcanoes.” Recent images captured by the Joan Oró Telescope at the Montsec Observatory in northeastern Spain reveal spiral jets emanating from the comet’s surface, suggesting that ice is sublimating as it approaches the sun. This behavior aligns 3I/ATLAS with other celestial bodies in our solar system, such as dwarf planets.
In another significant discovery, scientists have identified over 18,000 fossilized dinosaur tracks in Bolivia’s Carreras Pampa, making it one of the premier dinosaur track sites globally. The extensive area of footprints spans approximately 80,570 square feet (7,485 square meters), offering invaluable insights into the behavior and movement of these ancient creatures.
As our understanding of the universe and our own planet evolves, the implications of these discoveries resonate, prompting further inquiry into both our past and future. The intersection of ancient history and modern science continues to unveil the complexities of life on Earth and beyond.
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoUrgent Update: Tom Aspinall’s Vision Deteriorates After UFC 321
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Enhance Disaster Monitoring
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMIT Scientists Uncover Surprising Genomic Loops During Cell Division
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoAI Disruption: AWS Faces Threat as Startups Shift Cloud Focus
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoDiscover the Full Map of Pokémon Legends: Z-A’s Lumiose City
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoParenthood Set to Depart Hulu: What Fans Need to Know
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoGOP Faces Backlash as Protests Surge Against Trump Policies
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHoneywell Forecasts Record Business Jet Deliveries Over Next Decade
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Signals Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMaine Insurers Cut Medicare Advantage Plans Amid Cost Pressures
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYoshinobu Yamamoto Shines in Game 2, Leading Dodgers to Victory









