Science
Interlune Eyes Lunar Helium-3 Mining by 2028 for Clean Energy
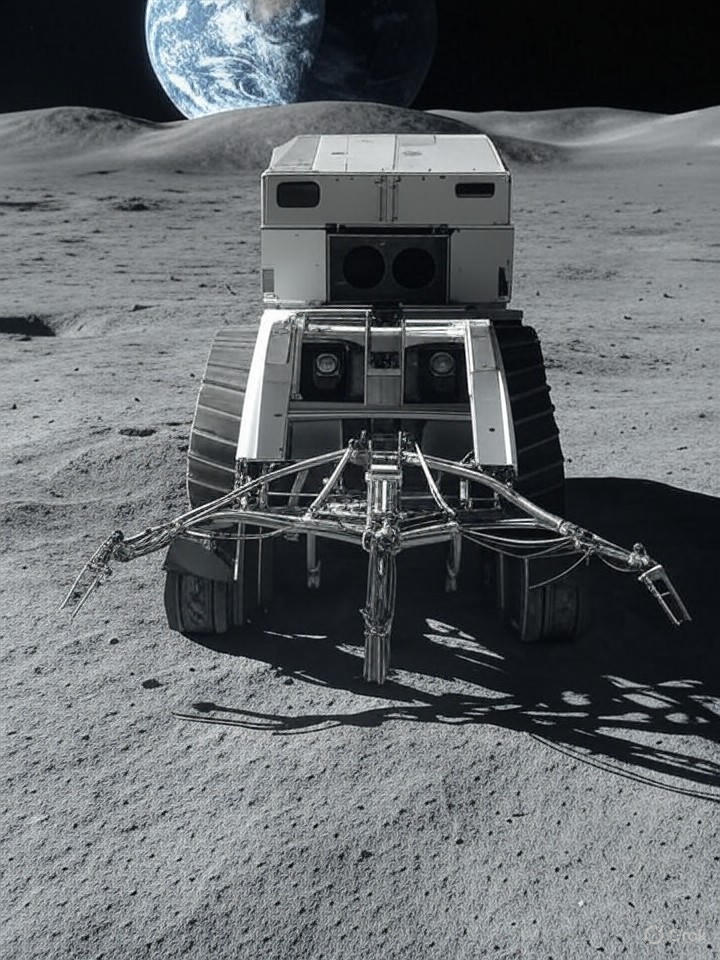
A major step towards the commercialization of space resources has been taken by the mining company Interlune, which has identified significant deposits of helium-3 on the lunar surface. This rare isotope, vital for nuclear fusion and other advanced technologies, could revolutionize energy production and various high-tech applications. The discovery marks a pivotal moment in the burgeoning field of space mining as both government and private entities seek to exploit the vast resources of the moon.
The announcement aligns with a growing trend of competition among global superpowers, particularly the United States and China, who are increasingly focused on securing lunar resources. According to a report from Space.com, helium-3 is expected to play a critical role in quantum computing as a coolant for maintaining ultra-low temperatures. Interlune has already forged agreements to supply up to 10,000 liters of extracted helium-3, showcasing early confidence in this emerging market.
Technological Advancements in Lunar Mining
Interlune’s progress includes the unveiling of a prototype harvester capable of processing 110 tons of lunar soil each hour, as covered by The Washington Post. This innovative machinery aims to overcome the logistical challenges of lunar operations, such as extreme temperatures and the absence of atmosphere, while also minimizing environmental disruption on the moon’s surface. The company plans to have its robotic systems operational by 2028, coinciding with major space missions like NASA’s Artemis program and China’s Chang’e missions. These initiatives could provide the necessary infrastructure for further exploration and resource extraction.
Helium-3’s potential applications extend beyond energy. The isotope is also crucial in medical imaging and supercomputing, where its rarity on Earth has driven up demand and prices. Insights from Forbes indicate that Interlune’s focus on autonomous mining technologies could transform the feasibility of lunar resource extraction.
Economic and Ethical Implications
Financially, the venture is gaining traction, with Interlune securing investments to deploy multispectral cameras for accurate resource mapping, as reported by Autoevolution. A significant collaboration with quantum cryogenics firm Bluefors highlights the growing interest in helium-3’s role in enhancing computational capabilities. The contract is one of the largest in the field of space resource extraction, underscoring the economic potential of lunar mining.
The ethical implications of lunar resource extraction cannot be overlooked. The Outer Space Treaty raises questions about equitable access to these resources, with critics cautioning against a new wave of colonialism. However, supporters, including voices from the European Space Agency (ESA), argue that advancements in technology could yield shared benefits, such as cleaner energy solutions that address climate change.
The potential for successful helium-3 mining has broader implications for a future space economy. As noted by 21st Century Tech Blog, this endeavor could pave the way for additional resource extraction, including water ice and rare earth elements, essential for sustaining long-term lunar settlements. If Interlune’s prototypes prove effective, the company could attract billions in investment, fundamentally changing how we view space from a scientific frontier to a lucrative domain.
The race for lunar resources is not merely about extraction; it represents a significant shift in our approach to utilizing cosmic materials. As technologies evolve, the dream of harnessing these resources moves closer to reality, with profound implications for energy production and technological advancement on Earth.
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoUrgent Update: Tom Aspinall’s Vision Deteriorates After UFC 321
-

 Health1 month ago
Health1 month agoMIT Scientists Uncover Surprising Genomic Loops During Cell Division
-

 Science4 weeks ago
Science4 weeks agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Enhance Disaster Monitoring
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoAI Disruption: AWS Faces Threat as Startups Shift Cloud Focus
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHoneywell Forecasts Record Business Jet Deliveries Over Next Decade
-

 Entertainment1 month ago
Entertainment1 month agoDiscover the Full Map of Pokémon Legends: Z-A’s Lumiose City
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoGOP Faces Backlash as Protests Surge Against Trump Policies
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoParenthood Set to Depart Hulu: What Fans Need to Know
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Signals Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYoshinobu Yamamoto Shines in Game 2, Leading Dodgers to Victory
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMaine Insurers Cut Medicare Advantage Plans Amid Cost Pressures








