Science
Researchers Identify Key Protein Driving Necroptotic Cell Death
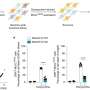
Researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have discovered a pivotal protein that triggers necroptosis, a form of inflammatory programmed cell death. This finding, published in the journal Nature, may pave the way for new treatment strategies targeting a variety of serious health issues, such as severe infections, sepsis, chronic inflammatory diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and certain types of cancer.
Necroptosis is characterized by the rupture of cell membranes, leading to inflammation and tissue damage. Unlike apoptosis, which is a more controlled form of cell death, necroptosis can contribute to various pathological conditions. The identification of this protein opens the door to understanding how necroptosis occurs and its implications for diseases like Crohn’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Implications for Treatment
The implications of this research are substantial. By targeting the identified protein, scientists may develop therapies that can mitigate the effects of necroptosis in affected tissues. This could be crucial for patients suffering from chronic inflammatory diseases, where uncontrolled cell death exacerbates symptoms and leads to further complications.
For instance, in conditions such as sepsis, where the body’s response to infection can lead to widespread inflammation and tissue damage, modulating necroptosis could help restore balance and improve patient outcomes. Furthermore, given the role of necroptosis in certain cancers, this discovery could facilitate the development of innovative cancer treatments.
Dr. [Name], a key researcher involved in the study, stated, “Understanding the mechanisms behind necroptosis is essential in addressing the inflammatory responses associated with many diseases. Our findings could contribute significantly to new therapeutic strategies.”
Future Research Directions
As researchers continue to investigate the role of this protein in necroptosis, further studies will be necessary to determine how exactly it can be targeted effectively in clinical settings. The research team plans to explore various pathways and mechanisms involved in necroptosis to identify potential drug candidates that could be used in treatment.
The potential applications of this research extend beyond just inflammatory diseases. By understanding necroptosis more thoroughly, scientists can also examine its relationship with neurodegenerative diseases and various cancers. This holistic approach may lead to breakthroughs that improve the quality of life for many individuals affected by these challenging conditions.
In summary, the identification of this key protein represents a significant step forward in understanding necroptosis and its role in human health. The findings from UT Southwestern Medical Center could ultimately lead to innovative treatments that change the landscape of care for serious illnesses associated with this form of cell death.
-

 Top Stories1 month ago
Top Stories1 month agoUrgent Update: Tom Aspinall’s Vision Deteriorates After UFC 321
-

 Science1 month ago
Science1 month agoUniversity of Hawaiʻi Joins $25.6M AI Project to Enhance Disaster Monitoring
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMIT Scientists Uncover Surprising Genomic Loops During Cell Division
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoAI Disruption: AWS Faces Threat as Startups Shift Cloud Focus
-

 Science2 months ago
Science2 months agoTime Crystals Revolutionize Quantum Computing Potential
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoDiscover the Full Map of Pokémon Legends: Z-A’s Lumiose City
-

 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoParenthood Set to Depart Hulu: What Fans Need to Know
-

 World2 months ago
World2 months agoHoneywell Forecasts Record Business Jet Deliveries Over Next Decade
-

 Top Stories2 months ago
Top Stories2 months agoGOP Faces Backlash as Protests Surge Against Trump Policies
-

 Politics2 months ago
Politics2 months agoJudge Signals Dismissal of Chelsea Housing Case Citing AI Flaws
-

 Health2 months ago
Health2 months agoMaine Insurers Cut Medicare Advantage Plans Amid Cost Pressures
-

 Sports2 months ago
Sports2 months agoYoshinobu Yamamoto Shines in Game 2, Leading Dodgers to Victory









